A UNEP report states that “the world is still heading for a temperature rise over 3°C this century.” It is astonishing to note that the world produces approximately 50 billion tonnes of CO2 every year. The agricultural sector is a significant emitter that contributes to around 10-14% of these emissions. Apart from this, it also involves farming practices that are resource-intensive and lead to land degradation. Therefore, it is essential to adopt regenerative agriculture to boost crop yields without causing any damage to the environment.

What is Regenerative Agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture incorporates farming practices like zero-carbon farms that seek to improve productivity and enhance biodiversity by reducing the carbon footprint. The fundamental principles include reducing soil disturbance, covering the soil surface through vegetation cover, incorporating diverse crops and living roots in the soil, and grazing livestock. These practices remove carbon present in the atmosphere and return it to the ground, thus converting the croplands into a ‘carbon sink.’

Regenerative Agriculture Practices and Carbon Sequestration
Biosequestration refers to capturing carbon from the atmosphere in soils, plants, water bodies, and other geological formations. This phenomenon decreases carbon dioxide, which is responsible for global warming. Due to the increasing concerns about GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions, organizations have adopted practices that lead to carbon sequestration. Some of these efforts are listed below:
- Reducing Tillage: Constant plowing or tilling leads to soil erosion and degradation. These activities also emit vast quantities of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The adoption of low-till practices reduces soil disturbance and carbon dioxide levels and creates a healthier environment for the crops.
- Nitrogen Fertilizers: Besides increasing crop yield, nitrogen also contributes to the process of carbon sequestration. Thus, farmers are now incorporating nitrogen fertilizers to improve soil organic matter while boosting results.
- Mulching: Farmers apply mulch, a layer of organic matter, to the soil to improve its fertility and reduce weeds’ growth. Additionally, studies have found that four years of mulching leads to an increase in carbon sequestration by 41%.
- Cover Cropping: This practice protects the soil from the erosion of wind and water with the help of impregnable roots. It helps the soil retain moisture, reduces the need for tilling operations, and leads to the growth of microbes that increase carbon levels in the ground.
- Biochar: It is a substance resembling charcoal produced by burning organic waste. The process releases no toxic fumes. Instead, it improves the soil structure and water retention capacity, thereby preventing the loss of vital nutrients. In addition, it provides stability to carbon, thus preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere.
- Compost consists of a mixture of organic ingredients used to provide fertility to the soil, made by decomposing food and plant waste. And it is rich in essential nutrients and microbes. Typically, compost application is in teas that are a mixture of organic manure and water. The process contributes to the development of microorganisms that capture carbon in the soil through photosynthesis.
- Agroforestry is a form of land management that integrates trees and shrubs with crops as part of regenerative agriculture. It provides soil protection through strong roots, shelters crops from rainstorms, and helps sequester carbon from the atmosphere.

The need for Regenerative Agriculture Techniques
Regenerative agriculture techniques usher in a host of benefits:
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Food production processes contribute to around 26% of the global GHG emissions that are a significant cause of global warming. Regenerative farming seeks to introduce techniques that lead to much reduced GHG emissions.
- Mitigates Climate Change: Carbon sequestration and decreased GHG emissions through regenerative land management techniques will help combat climate change.
- Reinvigorates Grasslands: Managed livestock grazing is an efficient regenerative technique to prevent the degradation of grasslands. At present, 70% of greens are degraded and have no use from the agricultural point of view.
- Improves Soil Health: We lose 24 billion tonnes of soil as a result of erosion every year. Studies have revealed that these regenerative methods lead to the growth of vital microbes that are the basis of healthy soil.
- Lesser Synthetic Chemicals: There is low usage of chemicals and harmful pesticides, and thus, there is less water pollution due to leaching.
- Ensures Food Security: Regenerative agriculture methods employ organic farming techniques that yield more produce even in less favorable weather conditions. Regenerative agriculture and consumer trends also support the recent consumer transition towards ethics-based and plant-based eating, Read more.
- Increases Profitability: Less investment in chemical inputs such as fertilizers, antibiotics, pesticides, and herbicides increases profit margins. Low, efficient usage of these products also boosts crop yields.
- Prevents Droughts: Regenerative agriculture practices increase the moisture retention capacity of the soil, thus tackling droughts in the long run.
Regenerative agriculture practices lead to carbon sequestration, thereby reducing the level of Greenhouse Gases present in the atmosphere. In this context, it is important to mention the concept of Carbon Offsets. It is a recently introduced scheme that allows companies and individuals to make investments in various environmental conservation projects across the globe to compensate for their carbon footprint. It aims to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing GHG emissions and inducing multinational companies to take part in conservation efforts.
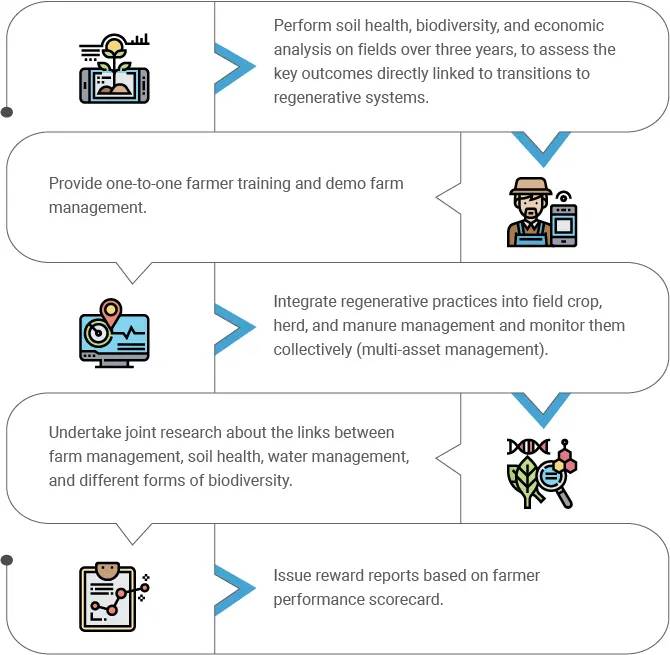
In the present scenario, several technologies are emerging that seek to boost regenerative agriculture practices through smart solutions. The agricultural sector is now increasing its reliance on ICT, robotics, automation, soil, and crop monitoring systems, and biotechnological tools for farm management.
Cropin, a leading AgTech company, provides smart solutions through applications like SmartFarm that simplify farm management. These tools ensure efficiency and productivity in agricultural practices while striving toward fulfilling sustainability goals. Cropin’s intuitive platform empowers farming companies to encourage regenerative agriculture among farmers.