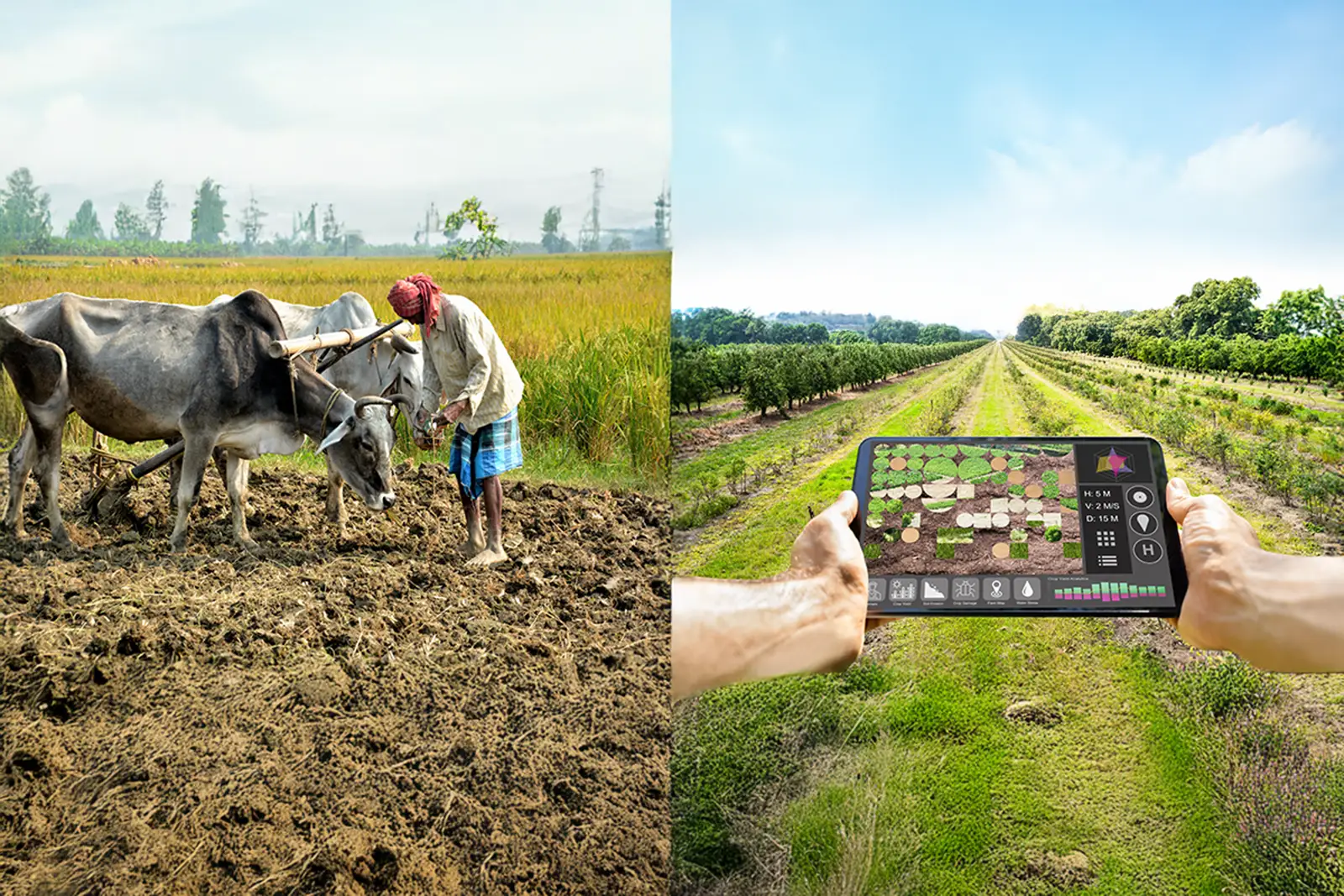
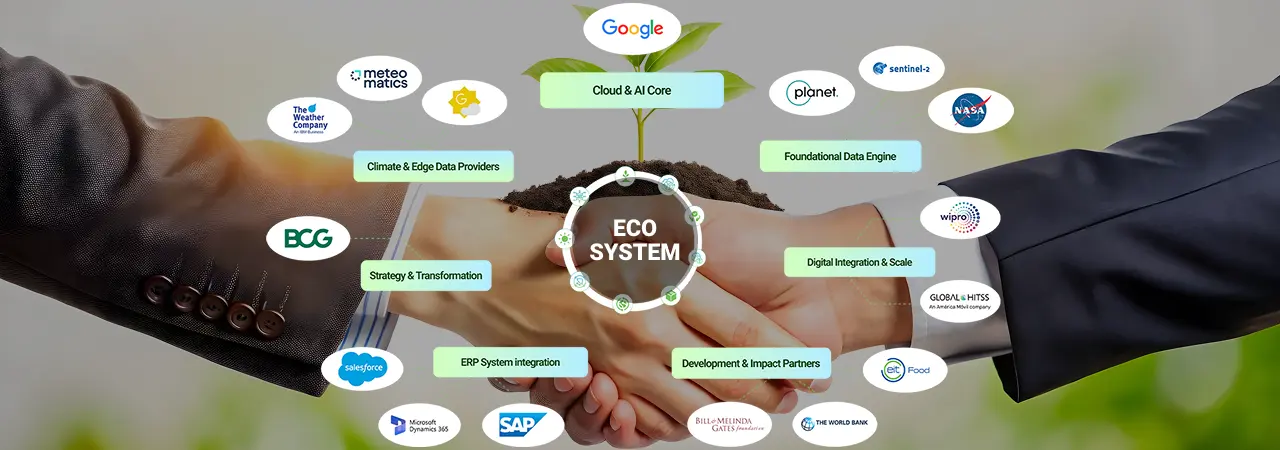
Many challenges, one solution: sustainable agricultural fueled by the power of technology
- Transparency and visibility across crop value chains
- Predictable yield
- Mitigate climate change and drive resilience to it
- Provide intelligence to manage the efficient use of agri-inputs
- Enhance productivity
- Decrease greenhouse gas emissions
Change management for sustainable agriculture
Root, adapt, thrive: change management roadmap for resilient sustainable agri-ecosystems
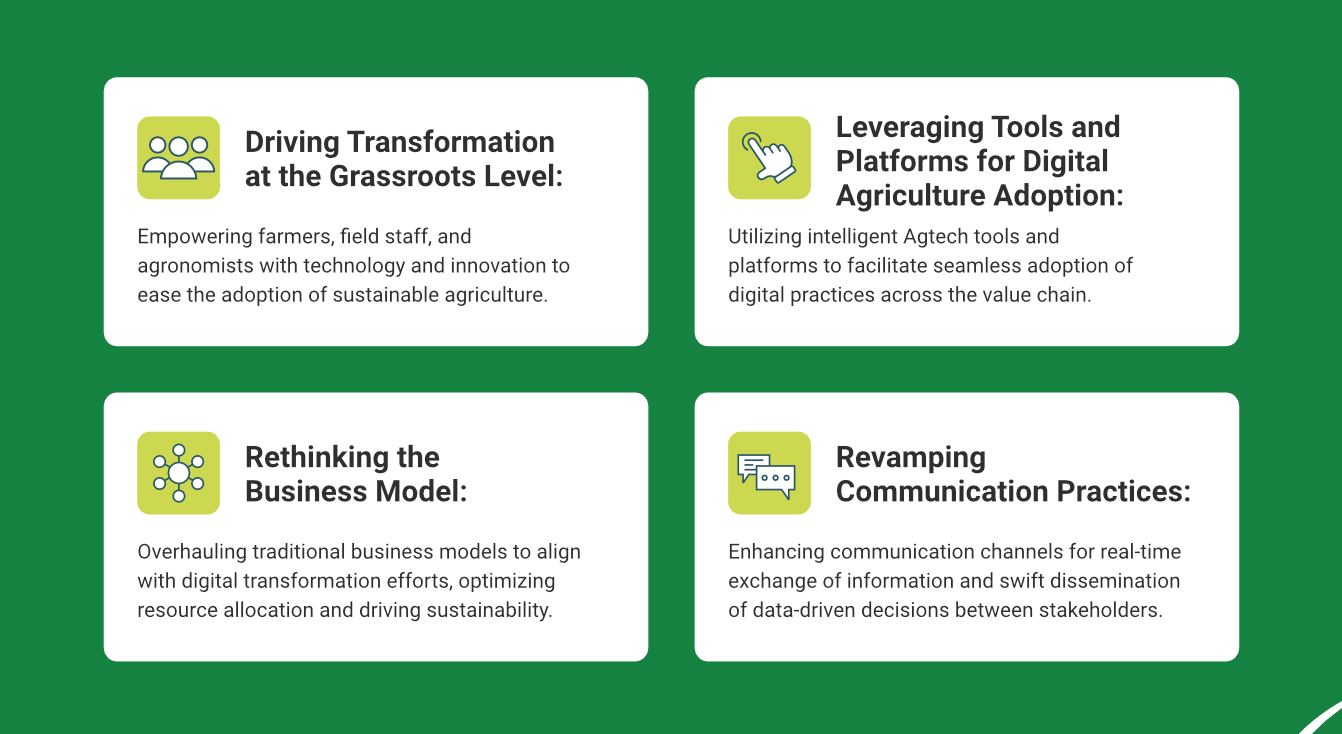
First step in change management: a transformation empowering the roots of agri-ecosystem
- Prioritize accessibility and user experience : The digital transformation must be driven through tools and platforms that are easy to learn and use, even for those with limited tech experience. The diverse demographics of stakeholders in agri-ecosystems necessitate simple-to-use interfaces available in multiple languages. They should be mobile-compatible as the first touchpoint—the farmers and field officers work on the field.
- Training and capacity building :Empowerment goes hand in hand with education. We must make these tools accessible and conduct relevant training programs to equip farmers, field staff, and agronomists with the skills and knowledge to harness technology effectively. This will help them maximize the potential impact.
- Data security and transparency : The data collated should be secure and accessible to enable informed decision-making. Enterprises must uphold transparent data-sharing practices to build trust within the agricultural community.
Change management techniques: leveraging platforms to ease adoption of digital agriculture
Deploying an intelligent Agtech platform is essential to achieving the vision of sustainable agriculture. However, for an agribusiness to effectively adopt technology, it first requires a comprehensive platform that connects multiple stakeholders, from farmers to top management. The platform should provide seamless collaboration and information sharing across the agricultural ecosystem.
Change management strategies- rethinking the business model
With grassroots empowerment and leveraging data-driven intelligence underway, the focus must now be on reimagining business models to align with digital transformation efforts. Enterprises must embrace a paradigm shift in management processes, leveraging data analytics and remote sensing technologies to monitor field operations and optimize resource allocation. This holistic approach enhances profitability and minimizes environmental impact, fostering a harmonious balance between economic viability and ecological sustainability.
Revamping communication practices
Scaling change and innovation
Technology as a change agent: empowering productive sustainable agriculture
Ease of adoption and user-friendly interface
Digitalization using the scalable, cost-efficient, and secure Cropin Cloud platform helps monitor, measure, and analyze individual farmers’, crops’, and fields’ unique needs. It provides hyper-local knowledge while paving the way to standardization at a global level for efficient agricultural management.
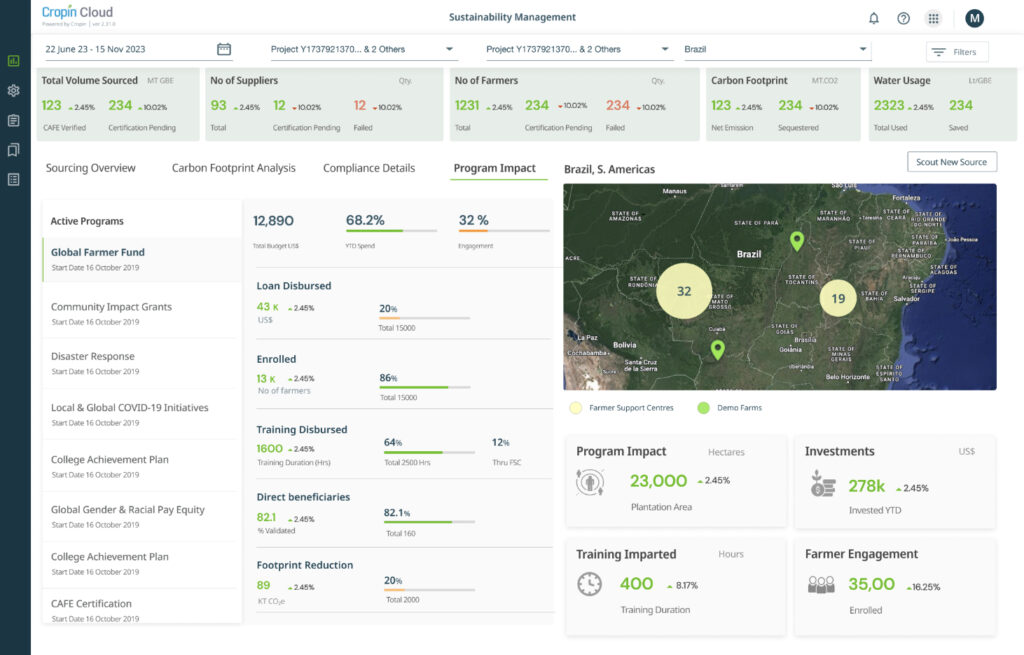
Reliable farm data management
Through its Data Hub, the Cropin Cloud platform integrates data from multiple sources to create reports that give in-depth insights into crop growth and harvests. Cropin utilizes near real-time data to derive intelligence that can alert farmers about crises like pest and weed infestation beforehand and enable quick resolution.
Market ecosystem enablement
Rational reporting frameworks
Adopting climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices like no-tillage, precision farming, intelligent land use, etc., will reduce agricultural emissions and help mitigate climate change. Monitoring standards and adopting legislation and regulations can ensure that the farming community practices sustainable agriculture. Digitizing farming practices on the Cropin platform enables constant digital monitoring and provides verifiable metrics for sustainability reporting.

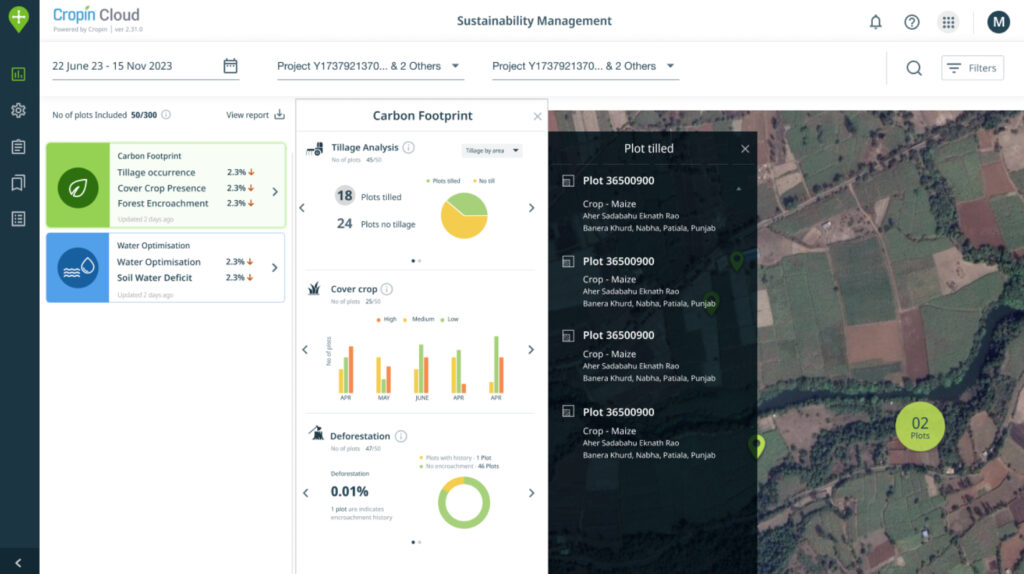
AI and data-driven program optimization
Cropin Cloud, an intelligent agriculture cloud, integrates real-time data from remote sensors like satellites, drones and in-field devices like soil sensors to generate AI/ML-driven intelligence. These models generate advisories and alerts to optimize agri-input usage and efficiently mitigate risks. It results in higher yield and quality, while production costs and workloads are reduced by analyzing data and improving forecasting.
Orchestrating change
In conclusion, agriculture, a prerequisite for human existence, must embrace sustainable practices that are in harmony with nature and not against it. Agricultural sustainability, which works on the ethos that we should cater to the needs of the present without compromising the prospects of future generations to meet their own needs, requires change management.