In this blog post, we will explore two closely related concepts: precision agriculture and smart farming. We will explore their common ground as digital farming methodologies and uncover the subtle differences that set them apart.
What is the difference between smart farming and precision agriculture
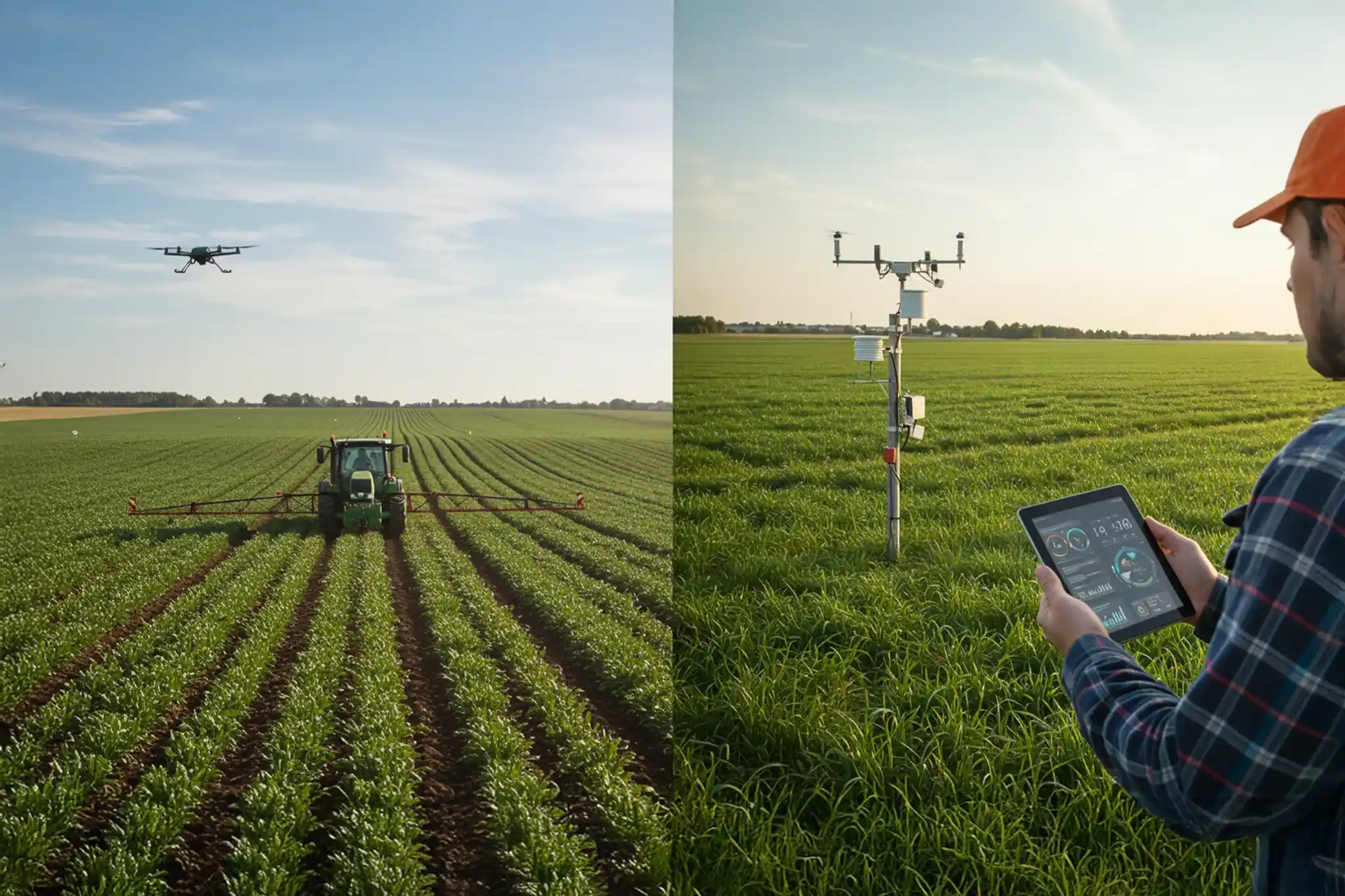
Smart farming is a comprehensive approach to agriculture that utilizes a diverse range of technologies. By integrating tools such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and automation, it creates a sophisticated and interconnected farming ecosystem. Precision agriculture is a subset of smart farming. This farm management approach uses digital techniques with a specific focus on monitoring and optimizing agricultural production processes. The key here is to optimize input resource management at the crop level, leveraging technologies like sensors and data analytics tools. It uses technology to collect data about the farm, such as soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, and then that data is used in the decision-making process to manage the farm. For example, as farms are heterogeneous, precision agriculture uses targeted fertilizer applications to specific areas of the field that need more nutrients and adjusts irrigation based on soil moisture levels.
Overview of smart farming
What is smart farming
What are the benefits of smart farming
Overview of precision agriculture
What is precision agriculture
As the name suggests, precision farming or precision agriculture involves highly controlled, accurate, and optimized agricultural production. It facilitates more efficient resource utilization, better yield, and reduced environmental impact, all at the same time. An ideal example of precision farming practice is a focused agrochemical application with AI-aided analysis that targets only areas that need attention instead of the blanket application.
IG steps in precision agriculture
Technologies used in precision agriculture
What are the benefits of precision agriculture
Precision agriculture offers many benefits for farmers. By precisely targeting specific areas of land, farmers can optimize resource use, leading to increased yields, reduced costs, and improved environmental outcomes. This site-specific crop management (SSCM) approach enhances profitability and contributes to sustainable climate-smart agriculture.
Challenges in adopting precision agriculture and smart farming
- High initial investment : Implementing these technologies often requires substantial upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure.
- Technical expertise : Operating and maintaining complex systems may demand specialized knowledge and skills that farmers may not possess.
- Interoperability : Ensuring compatibility between different hardware and software systems can be challenging.
- Data integration: Integrating data from multiple sources is essential for deriving comprehensive insights, but it can be challenging due to varying formats and standards.
- Internet connectivity: Reliable internet access is crucial for data transmission, especially in remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Data security and privacy : Protecting sensitive farm data from unauthorized access and ensuring data privacy is a top priority.
- Infrastructure development: To support the adoption of technologies, investing in infrastructure upgrades, such as improved internet connectivity and power grids, may be necessary.
- Data analytics and management : Analyzing and managing large volumes of data effectively requires specialized tools and expensive expertise.
Smart farming vs. precision agriculture: key differences
How artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming precision agriculture and smart farming
How is AI used in precision farming?
What is the role of machine learning in precision agriculture?
What is the role of robotics and automation in precision agriculture?
Future trends in smart farming and precision agriculture
What is digital agriculture
How can you use cropin’s solutions to advance your agri-operations?
Smart farming
Precision farming
Reduce the environmental impact of agricultural activities: Sustainability and precision agriculture go hand in hand. Implementing digital solutions is only a way to further align with the eco-friendly narrative. Inch-perfect application of fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides can prevent soil and water pollution due to chemical runoffs. Advisories on effective irrigation cycles and soil conservation techniques can also prevent the unnecessary depletion of these natural resources.