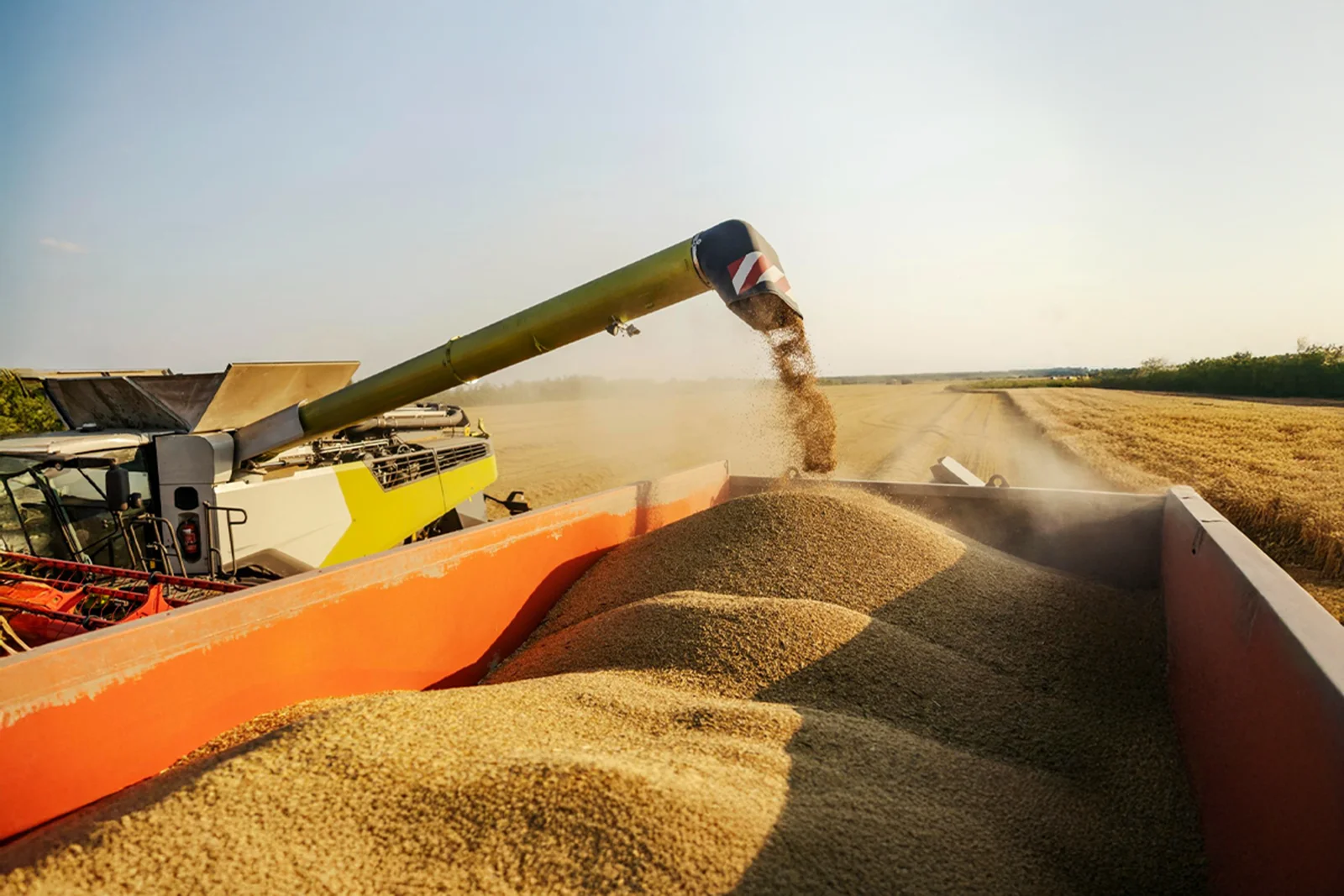
However, this journey is not one without crippling challenges. According to research, losses in the post-harvest sector are estimated to be anywhere between 10-25% in durables, semi-perishables, and products like milk, meat, fish and eggs. This number skyrockets to 30-40% when it comes to fruits and vegetables. Timely technological intervention with a strategic approach can cut down on losses–be it food or otherwise.
Post-harvest challenges seed companies encounter on a daily basis
Lack of digital records
- Prevent instances of carelessness and lack of proper hygiene during processing, packing, storing, and transportation
- Assure buyers seeds of high quality with minimum adulteration levels
Absence of seed traceability
- Help in capturing farm data at critical points post-harvest of seeds
- Establish end-to-end traceability of the seed life cycle
- Ensure seed authenticity and eliminate counterfeiting
- Provide access to new markets and build consumer trust with seed to shelf traceabilit
Poor compliance measures
- Establish quality benchmarks, eliminate counterfeiting (which accounts for about 30% of products in FMCG), and ensure that seed companies get the best quality of produce
- Ease in end-user traceability when required.
- Bring in transparency and build trust with the end consumer, boosting ROI and profits along the way
Pro tip: QR-code tools such as RootTrace provide tamper-proof and weatherproof stickers, making the end-product impossible to counterfeit. Seed companies must go back to the drawing board and ponder over investing in productive, ‘smart’ technologies that can eliminate key bottlenecks that hamper the quality and, by extension, the organization’s bottom line.
Improper inventory management
- Monitor logistics and keep the supply chain in check
- Keep track of customer orders and drive inventory accuracy
- Ensure end-to-end tracking with SKU tagging and enhanced visibility
- Improve quality control and packaging quality, and ensure better marketability
Monetary losses
The final word
“If post-harvest grain loss alone was completely eliminated, the world would gain virtual territory equivalent to three times the cropland area of France.” – McKinsey.
There are numerous advanced technologies and tools that seed companies can leverage today. Cropin’s data-driven and AI-powered smart agriculture solutions can keep the post-harvest losses to the minimum, ensuring compliance and transparency across the entire process. This can drive immediate and proactive correction of errors and ensure GMP practice, both during seed transit and while they are kept in storage. If seed companies want to extract optimum value and maximize profits throughout the seed value chain, adopting customized and sustainable technology is well worth the effort and investment.