Environmental impact of agriculture
- Agriculture contributes 13-18% of all green-house-gas (GHG) emissions
- Half of the world’s habitable land is used for cultivation.
- Agriculture uses 70% of global freshwater withdrawals.

Sustainable agriculture: good for the planet, farmers, and business
The eco-friendly arsenal of interconnected approach
The goal is to minimize our carbon footprint, conserve precious resources, and build farms that thrive alongside the planet, not at its expense.
What is sustainable agriculture?
The concept of sustainability rests on three interconnected pillars – economic, social, and environmental sustainability. The three pillars and effects of sustainable agriculture are closely linked. For example, when agri-inputs like fertilizer or water are precisely applied site-specifically, they save farmers’ resources (the economic aspect) and contribute to nature protection (the environmental aspect). This positively impacts the social aspect of the well-being of the community.
The business potential of sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture: a smart transformation of agricultural value chain
Cultivating a thriving future: how technology paves the way for sustainable farming
- Secure Traceability
- Farm analytics & management
- Crop area & yield estimation
- User-friendly dashboard
- Integration of solutions
- Streamlined communication
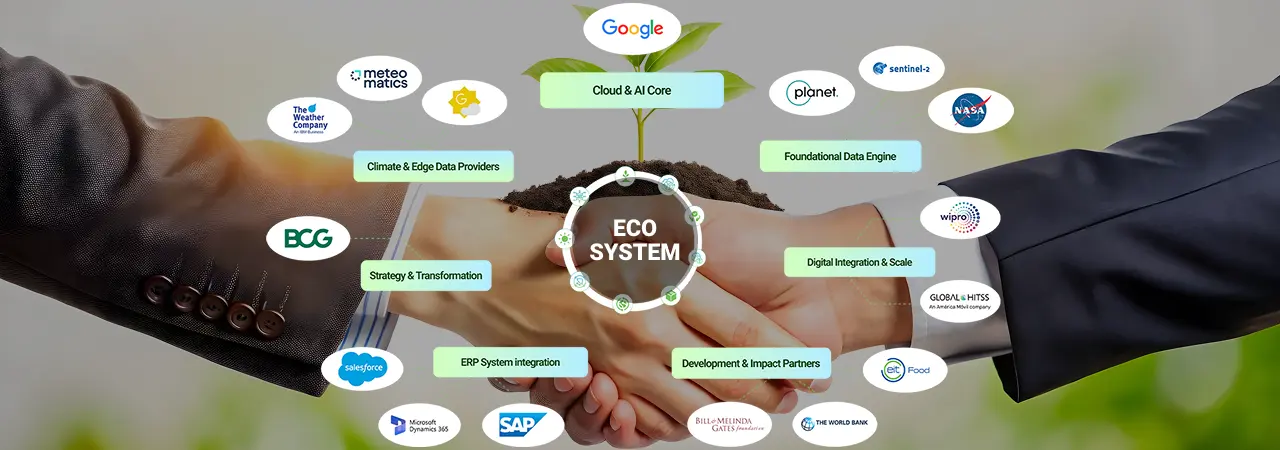
Harness the power of data with Cropin’s data hub
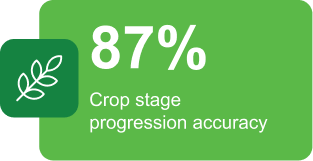
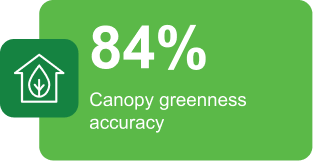
Actionable insights powered by Cropin’s intelligence
- Canopy Greenness
- Canopy Nitrogen Uptake
- Canopy Water Stress
From claims to validation: verify sustainability efforts with Cropin’s dMRV
Growing green, growing profits, real-world success stories: maximizing potato yields with Cropin
- 45-day accurate yield forecasts
- Optimized water usage through crop water stress monitoring
- Procurement planning based on crop progression and health
- Maximized productivity and reliable potato supply
Models used: Canopy Greenness Index, Canopy Water Stress, Crop Progression Model, Disease Early Warning System, and Disease Graph.
This case study demonstrates how data-driven farm management can empower food processors with predictability and sustainability in their potato supply.