Challenges on the road to farm digitization
- 54% indicated a shortage of digital talent and digital knowledge was a top challenge to successful farm digitization
- 51% stated that the lack of workflow customization and localization of digital solutions posed a challenge
- 41% of respondents said that unstructured data sets were a challenge to effective farm digitization
- Ensure adherence to Package of Practices (PoPs) and produce quality for commanding market premium
- Monitor and track agri-input resource usage to ensure food safety and integrity
- Provide end-to-end traceability of operations to guarantee certifications across existing and new markets
- Prevent counterfeiting of goods with QR-enabled product stickers
An offering with a difference: Cropin Cloud
- Easy and user-friendly interface that do not require unique skillsets and can be used by stakeholders at all stages of the value chain
- Intuitive workflow customization and comprehensive localized intelligence
- Integrated data management and actionable intelligence
The Cropin advantage
Learn how a leading food and beverage enterprise deployed Cropin Cloud to digitize and transform farm operations and use plot-level predictive intelligence to increase yield, predict diseases and improve operational efficiency
Democratizing data access
ESG compliance: an extra benefit
In addition to comprehensive tracking the crop from farm-to-fork, Cropin Cloud empowers businesses to track environmental impact of agricultural production, along with its economic, health and social consequences. Cropin Intelligence uses contextual deep-learning and AI/ML models developed by the platform to provide agri-businesses with transparent data points to ensure sustainable agriculture. The apps on Cropin Cloud platform record multiple high quality data points during crop lifecycles like soil data, harvest quality and quantity, crop images, irrigation details, pest and disease incidents, details on usage of agri-inputs like fertilizer and pesticides, sowing date, seed variety, all weather parameters, satellite data and various agronomic data records/observation at different crop stages. This rich data lake so collated not only allows the enterprise customer to get a 360-degree view of all the agricultural inputs going into the cultivation, but also provides access to genuine, honest reportable data. This single source of truth can be used by the food processing companies as proof for alignment with their environmental, social and governance (ESG) goals.
Author Bio
Aditya Shah
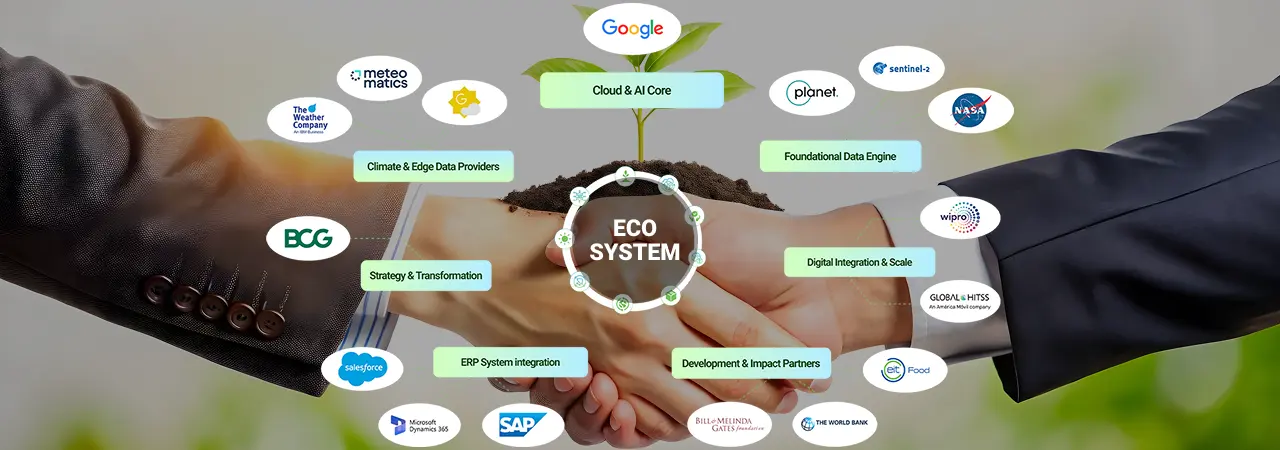
Aditya Shah is the Global Director of Strategic Partnerships and Business Head for APAC at Cropin, where he plays a key role in shaping the company’s global growth strategy through innovative collaborations. With over a decade of experience, he has been instrumental in establishing high-impact partnerships with industry giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft, bolstering Cropin's technological leadership. Aditya also spearheads strategic collaborations with development organizations such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the World Bank to drive positive impact for marginalized farmers. A creative thinker, he passionately advocates for blending attitude, skills, and knowledge to fuel true innovation across the agri-food ecosystem.