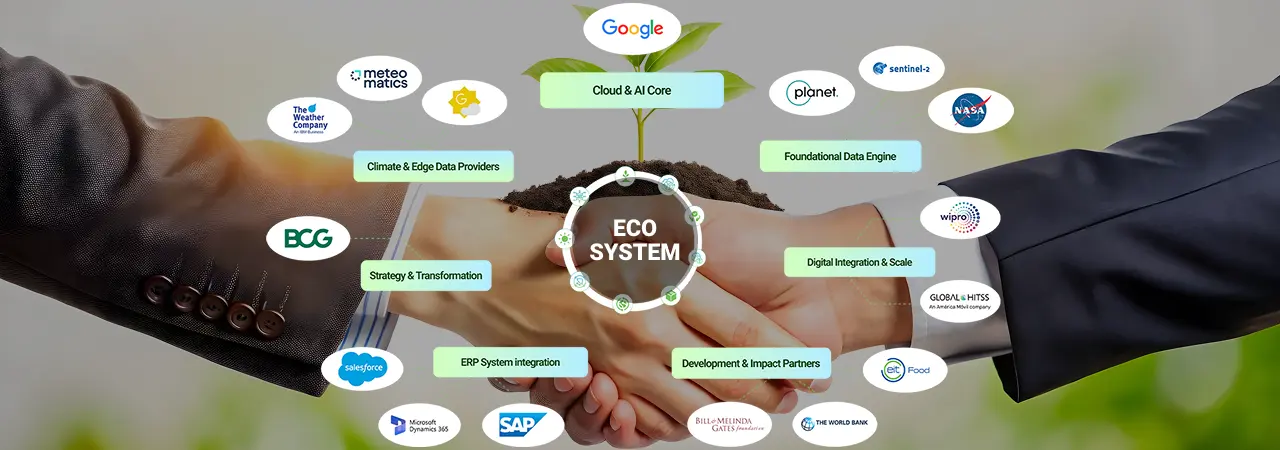
Synopsis:
Importance of sugarcane in the global economy
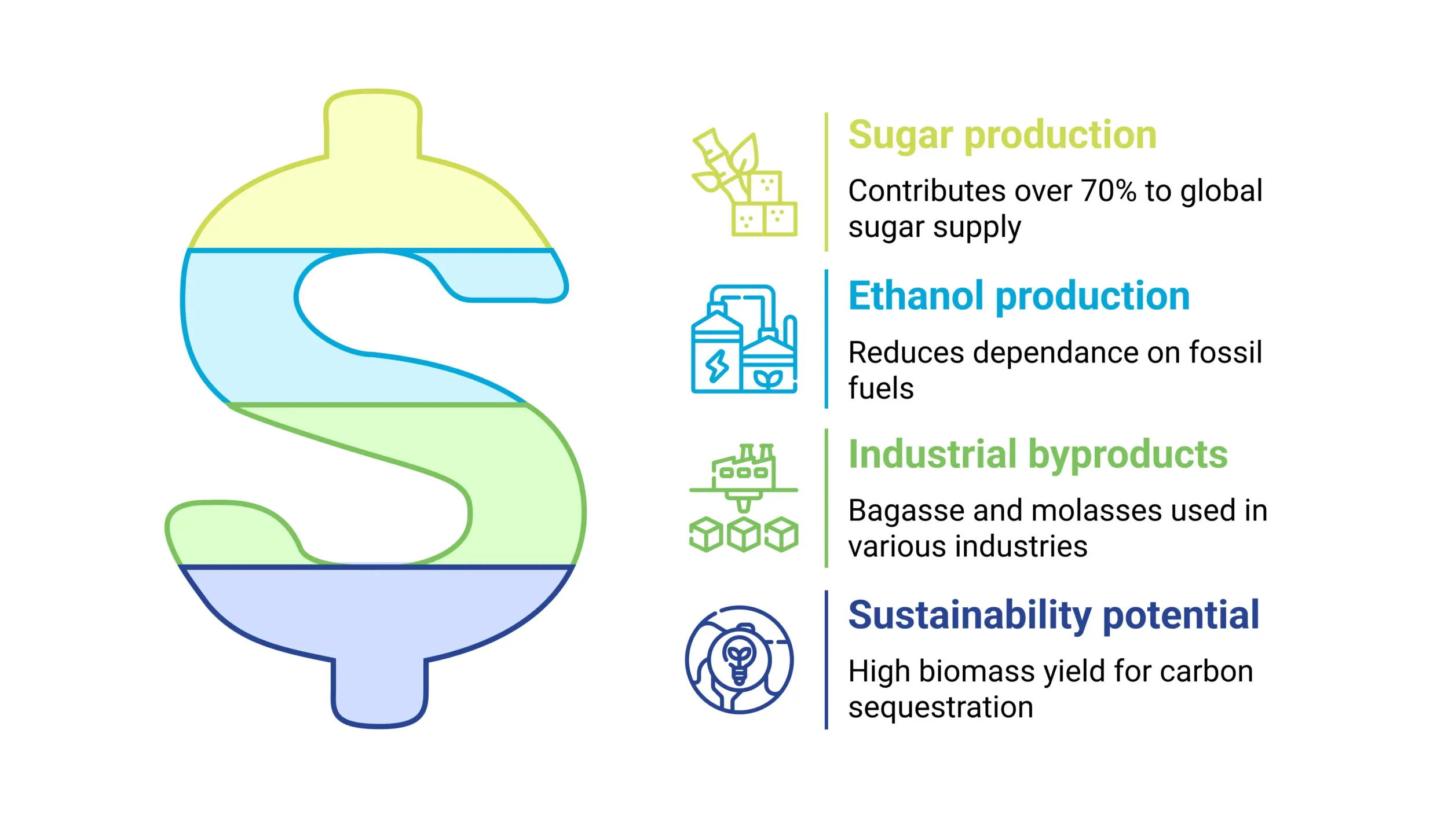
Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) is one of the most important commercial crops in the world. It is currently valued at $63.4 billion and soaring toward $88.6 billion by 2035. This tropical grass is the backbone of multi-billion-dollar industries. It accounts for more than 70% of the world’s sugar, with uses stretching into ethanol, renewable energy, and paper all while supporting the livelihoods of millions of farmers across more than 80 countries. However, this sweet crop comes with its challenges.
Why sugarcane matters
What are some challenges in sugarcane cultivation
- Climate change & extreme weather patterns
- Pest & disease pressure
- Rising input costs and environmental concerns
- Market volatility & pricing
- Sustainability & environmental impact
- Operational inefficiency
- Resistance to the adoption of innovation & technology
- Water scarcity across many regions
- Intensive monoculture leading to soil depletion
What are sugarcane growing conditions
- The Recipe for success: This tropical grass demands high solar radiation and heat, abundant water, and rich, well-drained soil (pH 6.0–7.0).
- Temperature check: The sweet spot for optimal growth is around 22°C-30°C daily mean temperature. Prolonged exposure below 20°C or above 40°C reduces the final yield.
- Quenching thirst: Sugarcane needs around 1000-1500 mm of annual rainfall. When water is scarce, growth slows and the crucial sugar content decreases—a problem solved by irrigation in drier regions.
- Soil needs: The biggest threat to its health is waterlogging, which stunts growth and invites rot. Farmers must ensure the soil is loamy and well-drained, avoiding excessive moisture to keep sugar levels high.
Data-driven field selection using cropin cloud platform
Choosing regions and plots with ideal temperature, humidity, and soil moisture is critical. Cropin Cloud platform offers data-driven regional insights on historical climate trends, active agriculture areas, suitability, sown areas, acreage, and yield potential of sugarcane to help select the best regions for cultivation/sourcing. A further deep dive at the granular plot level can be done to enhance decision-making.
Pre-planting practices
Don’t forget crop rotation!
- Farm and farmer details
- Crop rotation history
- Irrigation
- Tillage
- Green manuring
- Soil test & more
Planting
Planting is timed with the onset of rain to ensure sufficient moisture in the soil. Late summer and early fall are the best times to plant sugarcane.
Sugarcane is propagated through stem cuttings known as setts. Each sett should have 2–3 healthy buds. Using disease-free setts ensures a quality harvest. Dipping setts in fungicidal or hot-water solutions prevents seed-borne infections.
The digitization twist
Using historical and current weather insights, Cropin’s AI/ML models compute optimal sowing dates. Digitization on Cropin’s farm management app Cropin Grow enables complete visibility of field activities. You can
- Configure the best “Package of Practices” (PoP)
- Share timely alerts on PoP with farmers
- Monitor adherence of PoP & maintain logs
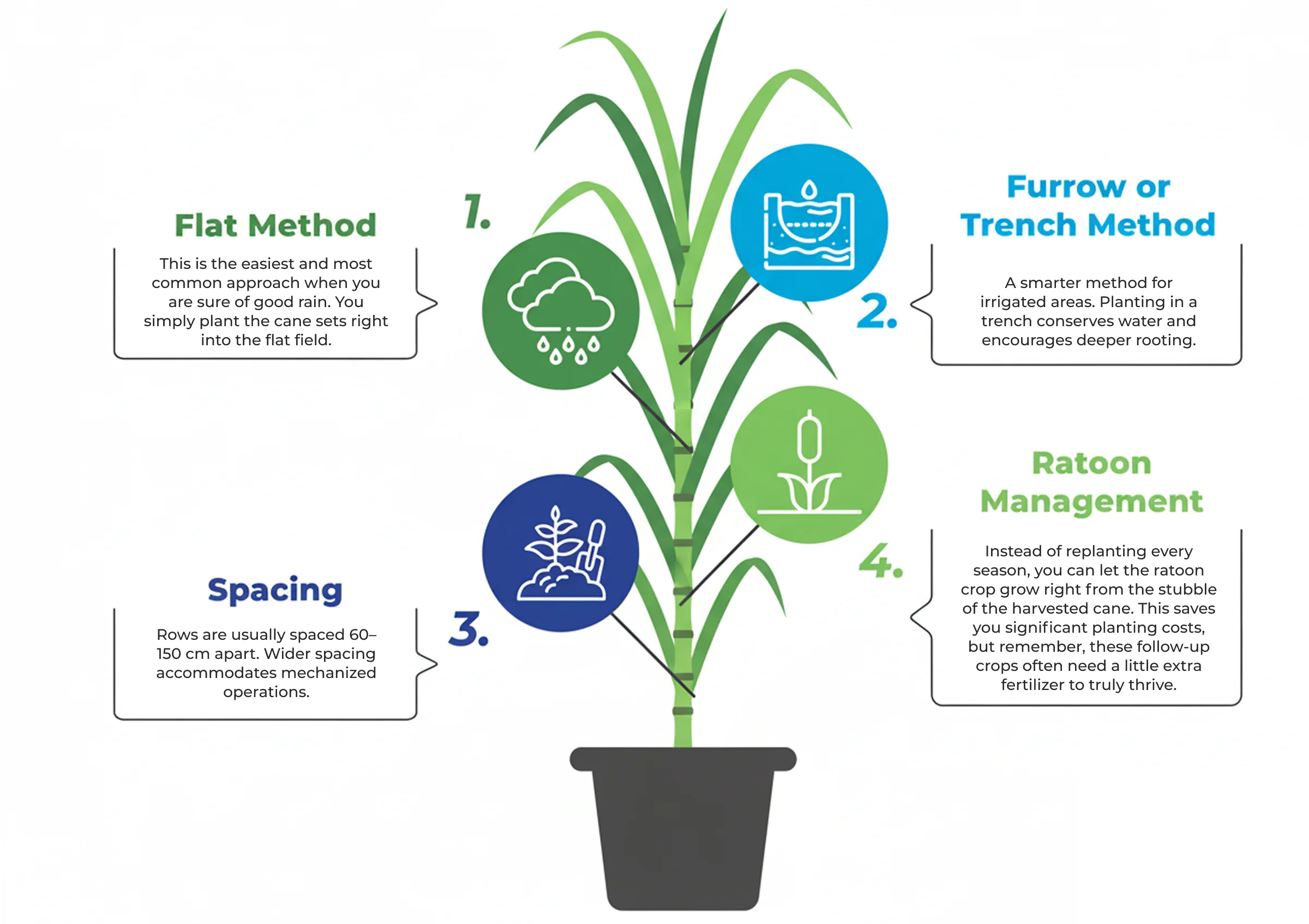
Planting methods
Growth stages in sugarcane cultivation
Cropin’s Disease Early Warning System (DEWS) continuously monitors weather conditions to predict disease occurrences at least 15 days ahead. This provides ample time for mitigative efforts and pathogen threat management.
To safeguard your crops, Cropin’s DEWS provides an AI- and satellite-driven early disease forecasting solution that enables farmers and agribusinesses to detect potential disease outbreaks well in advance.
Nutrient management for high yields
The digitization edge
Cropin: complimenting traditional farming with agri-intelligence
- Crop stage: This model predicts the current stage of the crop and the percentage progress of the crop from sowing based on heat units using remote-sensing capabilities, weather data, and crop science. Based on the crop stage, nutrient management can be planned. Cropin also offers insights into whether the harvest is on time, slow or fast paced, and if the crop is healthy and progressing towards maturity. This helps identify harvest deviation, the causative factor, and mitigative efforts.
- Crop health monitoring: Cropin defines crop health using the following parameters:
- Canopy Greenness (derived from Normalized Difference Vegetation Index): Measures photosynthetically active biomass, detects crop health, guiding fertilization
- Canopy Nutrient Uptake (derived from Normalized Difference Red Edge Index): Aids nitrogen management
- Canopy Water Stress (derived from Land Surface Water Index): Helps plan irrigation
These are categorized into buckets and help detect changes in growth progression to plan and fine-tune fertilizer use, reducing costs and environmental impact. Cropin’s zone sampling feature helps adopt precision agriculture with the variable rate application (VRA) method. enhances the accuracy of yield estimation.
- Cropin DEWS: Cropin DEWS indicates the probability of disease occurrence based on crop science and past and forecasted weather data (temperature, humidity, precipitation). We will delve deeper into DEWS in the following sections.
- Yield estimation: Cropin’s advanced yield estimation model integrates our proprietary crop knowledge grid, remote sensing capabilities, weather data, and crop science to estimate yield. The model gets hypertuned at crop/variety/location levels. Yield estimation insights are offered 30-45 days before harvest. The zone sampling feature improves the accuracy of yield estimation. The advanced yield estimation insight is crucial for procurement planning, logistics management, and adjusting sourcing strategies.
Irrigation and water management with Cropin
Pest and disease management with Cropin
How can you beat these threats?
Do contact us for further information on Sugarcane-specific agri-intelligence.
Senescence: harvesting and post-harvest practices
How do you know when sugarcane is ready for harvest?
- Post-harvest handling: Once the cane is harvested, it must reach the mill within 24 hours; any delay means the sugar starts to degrade.
- Residue management: Instead of burning cane trash, smart farming relies on mulching to improve soil organic matter.
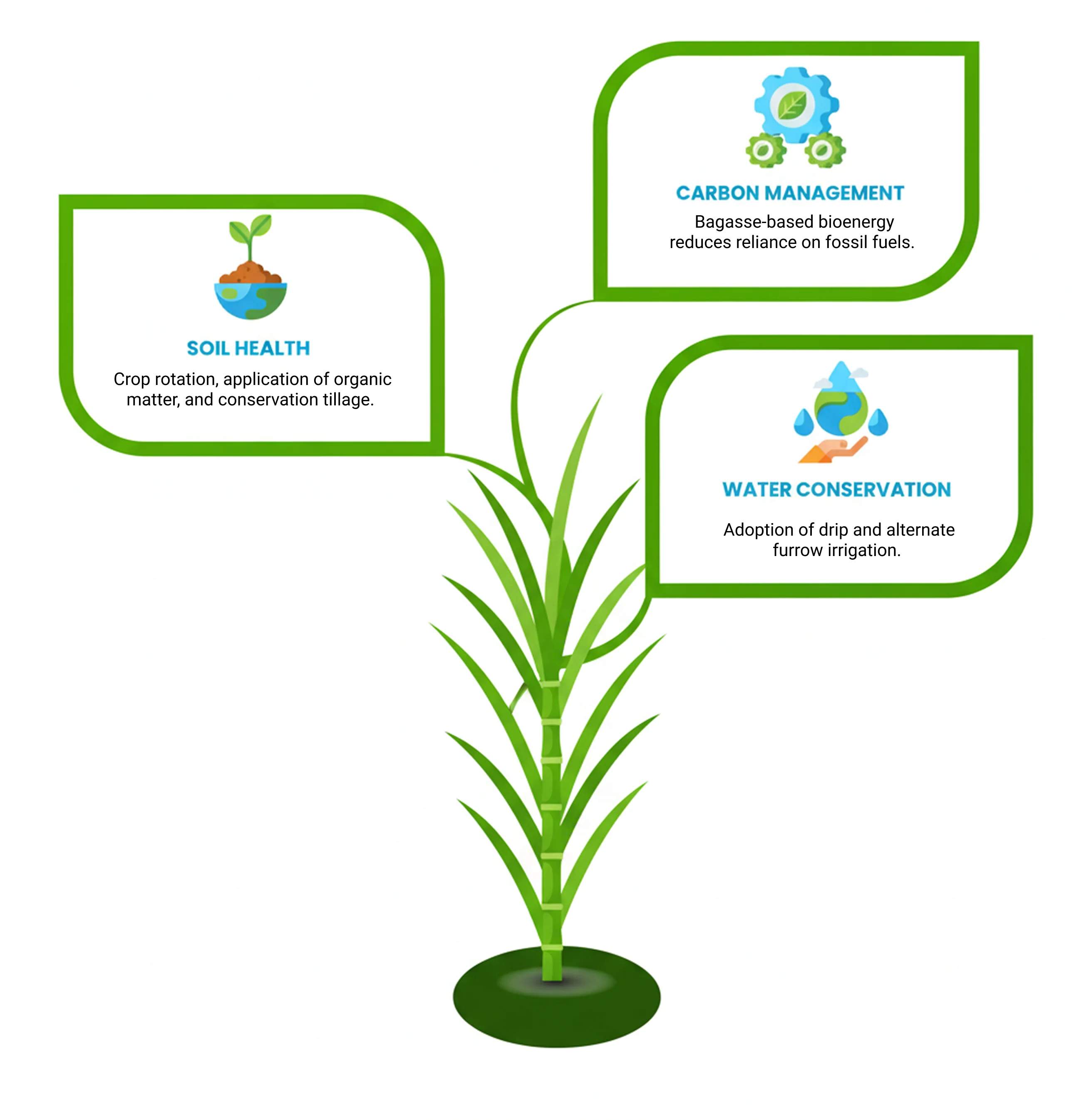
Sustainability and climate-smart sugarcane farming
Sustainable sugarcane cultivation isn’t just a trend; it’s how you protect your crop—and your business—from climate risks. It starts with simple practices:
The indispensable role of agritech in the future of sugarcane cultivation
- Remote sensing & satellites: Monitor crop vigor, stress, and growth stages across large areas
- IoT & sensors: Track soil moisture, weather data, and nutrient levels in real time
- Predictive analytics: AI models forecast yield, pest outbreaks, and irrigation needs
- Supply chain visibility: End-to-end digitization ensures traceability from field to mill, improving transparency for stakeholders
- Farmer empowerment: Mobile apps and digital advisory platforms deliver real-time, location-specific advisories to farmers
Conclusion:
The path forward is clear: leverage scientific crop management with digital agriculture solutions. From precision irrigation and digital alerts to predictive forecasting and supply chain transparency, technology providers like Cropin are actively transforming sugarcane farming into a smarter, more profitable, and truly climate-resilient enterprise.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Where does sugarcane grow?
What are the growing conditions for sugarcane?
What are the growth stages in sugarcane cultivation?
- Germination: Leaves appear on the planted cuttings that usually have three or more buds
- Tillering: The first sprouts appear. Tillering can last from 4-8 months, depending on the variety
- Stem elongation: Tiller stabilizes, cane formation, and elongation occur. The phase also marks rapid leaf production and the appearance of 4-5 internodes per month
- Maturation and ripening: Determined by the sucrose level in the stems. Stems should accumulate at least 8-12% of sugar by harvest
- Senescence: This is the last stage of the sugarcane growth cycle. The plants are fully ripe and ready for harvesting
How to improve the yields of sugarcane?
Author Bio
Haripriya Muralidharan
Haripriya Muralidharan leads content marketing at Cropin Technology Solutions, bringing a unique scientific rigor to brand storytelling. With a Master's in Chemistry from Pune University and research experience in cancer immunology, she discovered her passion in storytelling. For two decades, she has operated at the intersection of content, communication, and brand strategy, specializing in turning complex ideas into impactful narratives. Prior to Cropin, Haripriya leveraged her creative skills at Elsevier’s Chemical Business News Base and shaped multi-format content strategies for B2B marketing at Scatter.