The rich diversity and nutrition of the soil fade away due to years of farming. Thus, to conserve fertility, it has become essential to combine agriculture with technology. In this era of digitalization, the agriculture sector is encountering a radical transformation and relies on precision agriculture. It involves sensors, robots, GPS, data-analytics software, etc., to produce healthier crops and higher yields. It holds promise for the sector to ascend to the next level of productivity and profitability. Precision agriculture further welcomes the concept of IoT in agriculture.
Smart agriculture using IoT (Internet of Things), smart agriculture reduces costs, boosts efficiency, maximizes results, saves water and energy, and more. It helps cultivators meet the requisite conditions to increase crop yield and health, thus contributing to sustainable agriculture.

How Does IoT in Agriculture Monitor Soil Health?
Critical factors such as the need to match food production to meet the rising population’s demands, existing threats to food security, and climatic changes that affect crop production urge farmers to look for innovative approaches to increase efficiency and productivity.
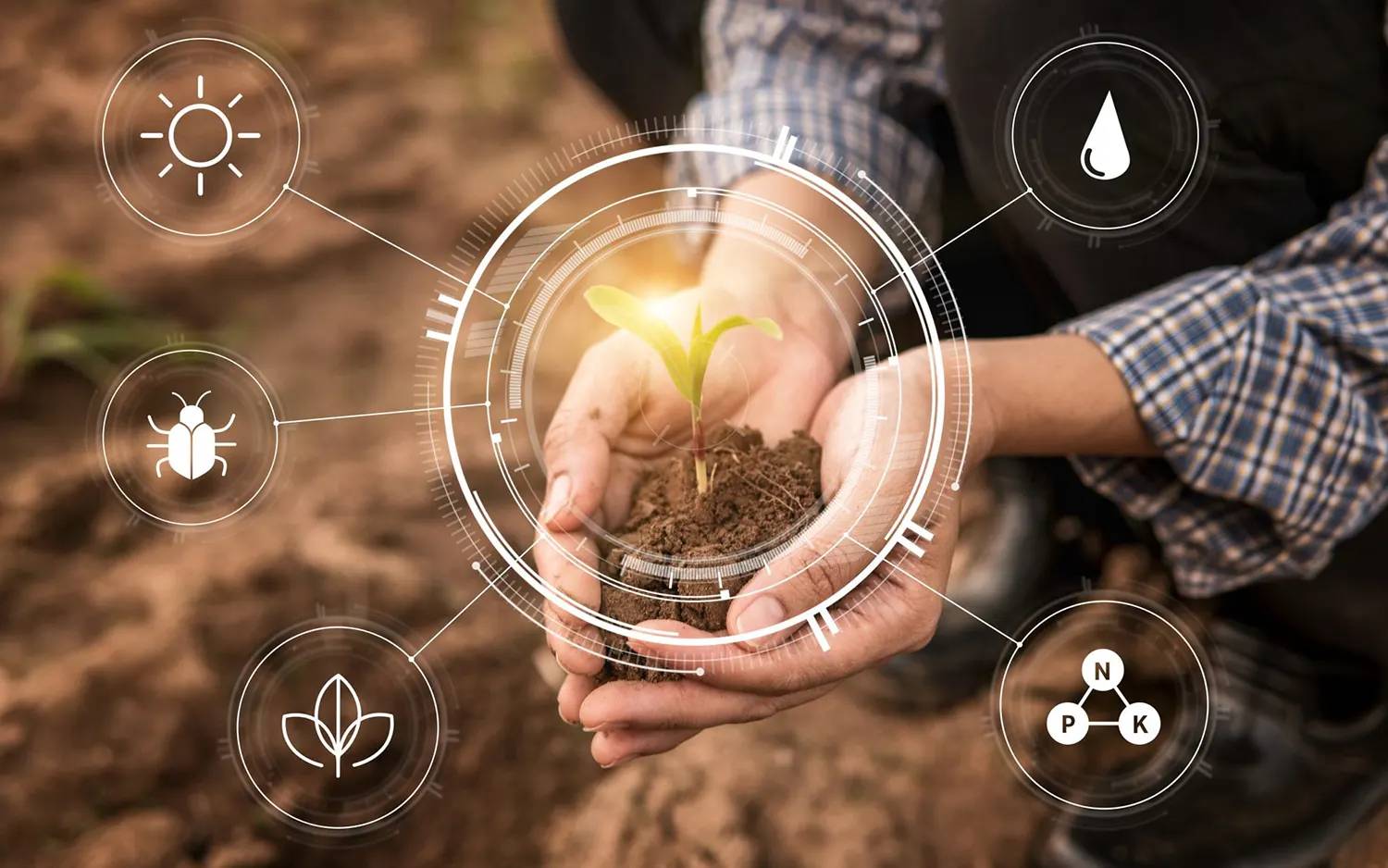
The top priorities of smart agriculture using IoT focus on weather, soil temperature, moisture, nutrients, and crop conditions. Let us review some of them.
- Soil Temperature: Soil temperature influences the growth of the root, respiration, decomposition, and nitrogen mineralization. Farmers need to ensure the most optimum temperatures when planting and cultivating crops to ensure higher productivity. Temperature sensors placed beneath the ground level and enabled with wireless technologies like infrared when placed strategically can provide farmers with real-time updates on soil temperature.
- Soil Moisture: Water is a critical nutrient for all plants and fundamental for the process of photosynthesis. Soil moisture also does the task of regulating soil temperature and hence heavily influences crop growth and yield. Buried probes with electrodes help monitor soil moisture content effectively. IoT sensors that estimate soil moisture can monitor and automate irrigation while also gathering humidity and temperature data of the soil.
- NPK Measurements: IoT sensors can also measure the soil nutrient content, namely nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Farmers can detect nutritional deficiency and determine if they need to fertilize the soil with additional nutrient content to increase crop fertility. These sensors are considerably new in the market and use several technologies to maximize accuracy. Besides monitoring NPK content, these sensors help detect the pH level and chemical composition of the soil. As these sensors can monitor changes in soil nutrients in real-time, they find applicability in farmlands, greenhouses, and soil research, too.
- Solar Radiation: Another application of IoT in agriculture is to measure the different types of solar radiation. Solar radiation is the amount of heat that reaches the earth from the sun. It is essential for photosynthesis and, thus, has a significant impact on crop productivity. The amount of radiation that soil receives and absorbs also affects soil temperature fluctuations and soil moisture evaporation. IoT sensors enable cultivators to measure photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), ultraviolet (UV) rays, and shortwaves to understand the correlations and trends.
- Weather: Farm productivity is affected by environmental factors such as rainfall, wind direction and speed, humidity, temperature, and air pressure. IoT-based connected devices allow growers to collect data periodically, automatically, and remotely. They provide deep, data-backed insights on farming conditions, which makes farming more precise and scientific. It also enables growers to optimize resource usage, reduce wastage, and save labor, time, and money.
As we mentioned previously, IoT sensors provide real-time data, which is helpful for both agribusinesses and farmers. They reduce manual labor, usage of water and energy, maintenance costs, and more. Other applications of IoT in agriculture are:
- They can review crop performance instantly using sensor mapping and intelligent dashboards.
- They can receive automatic reminders via SMS, push notifications, or emails.
- Farmers can securely store these data points for future use.
- Farmers can track patterns based on previously collected data to make informed decisions.
- IoT devices can integrate with other sources of data, such as farm management software.
- For relevant and up-to-date information, IoT sensors run cloud calibration.
What Are the Benefits of IoT-based Monitoring?
IoT is the central component of precision farming. It empowers cultivators to increase yield, minimize damage due to pests and diseases, and optimize resource usage. The data from the IoT devices are transmitted to make subtle adjustments for immeasurable benefits.

Below are a few of the several advantages of smart agriculture using IoT.
- Wireless Communication: IoT with extensive mobile coverage supports LoRaWAN, 5G, Zigbee, WiFi, satellite, and more. It provides smart agriculture solutions to farmers from urban, rural, and remote environments. Also, as the low-power IoT systems (nodes and sensors) run on batteries, solar, or other renewable energy sources, they are cost-effective in the long run.
- Water Conservation: The World Wildlife Fund states that agriculture and farming consume 70% of the world’s freshwater, but about 60% of this goes to waste due to several reasons. IoT in agriculture helps conserve water by ensuring that farmers use the resource judiciously and prevent the depletion of groundwater reservoirs, too.
- Prevents Over- or Under-watering: Over-watering hampers the oxygen levels of the roots and shuns crop growth. It even causes root rot in some plants, and as a result, they eventually die. Likewise, under-watering causes plants to grow slowly with leaves edges that are brown and dry. Some plants may even fail to flower entirely. Ultimately, poor plant health leads to death.
- Cost-effective and Time-saving: IoT devices serve the purpose of periodical testing. Farmers can rely on these devices to check the humidity level and temperature of the soil, and save a lot of time and resources. They can choose the ideal crop for the prevailing conditions to ensure productivity and profitability. The devices are affordable and do not require special skills to use and maintain these devices.
- Accuracy: IoT-based devices provide real-time data that are accurate, up-to-date, and automated and thus are more efficient than manual testing. Besides, they present a deep understanding of soil health and help producers to take action accordingly.
IoT devices unearth critical data for further research and understanding by agronomists, farmers, and agribusinesses. Nonetheless, this data is most valuable when the end consumers can view them as actionable insights.
To achieve this, Cropin’s SmartFarm Plus uses AI and data analytics to assimilate data from multiple sources, including third-party ERP solutions, manual input using the SmartFarm app, earth observation and satellite-based weather data, drones and other IoT devices. SmartFarm Plus leverages new-age technologies to deliver superior decision support at multiple levels to help advance agri-productivity for enterprises globally.